Indus River: The Indus River is one of the most important rivers in the Indo-Gangetic Plain of the Indian Sub-continent. The river Indus flows through India, China and Pakistan. The river originates in the Tibetan Plateau near the Mansarovar lake and flows through the Ladakh area of India and then flows along the entire length of Pakistan and at the end merges with the Arabian Sea.
Top 10 Largest Rivers in India, you would also find the details about Indian River Systems and major rivers of India.
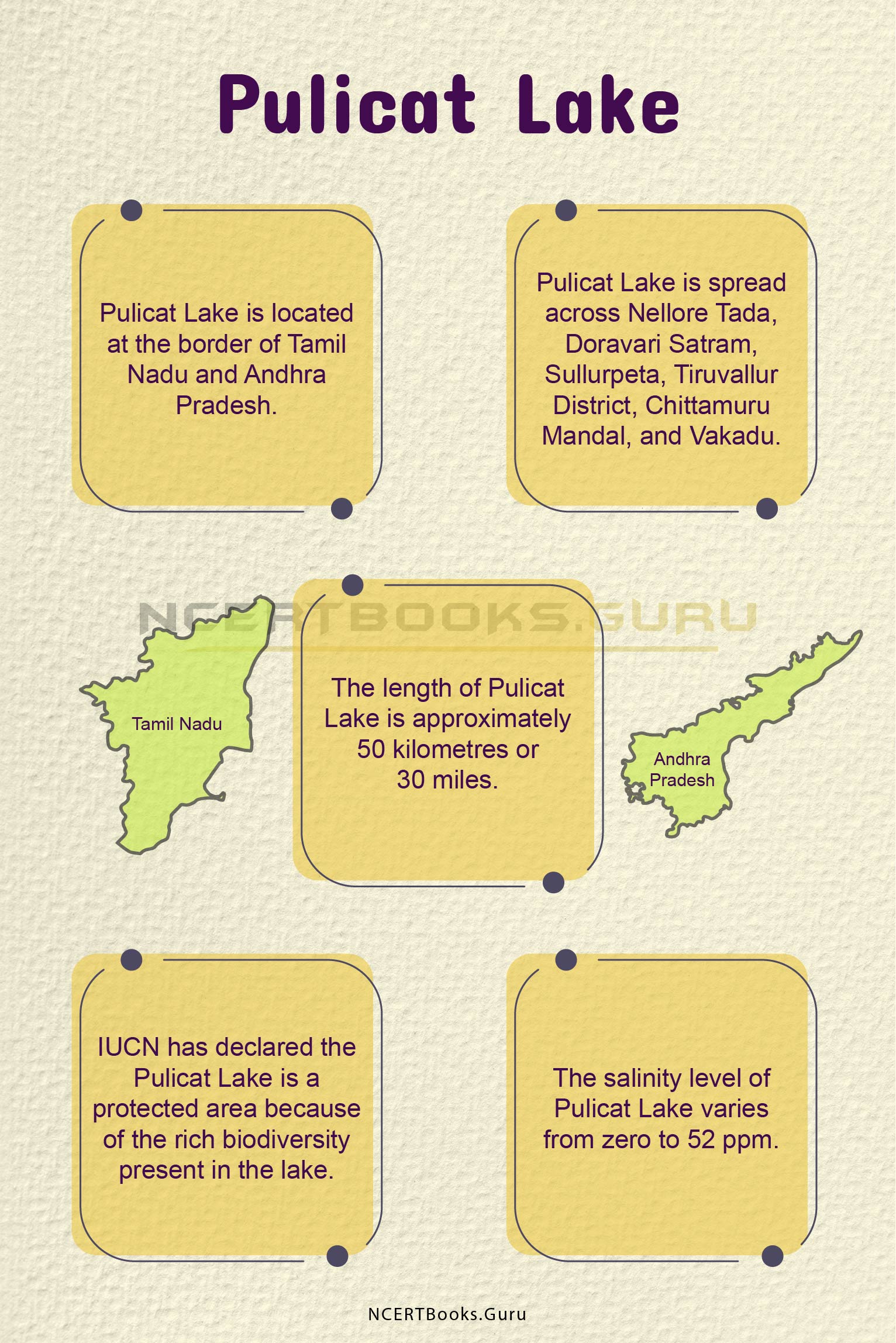
Indus River Details
| Origin | Originates from the Tibetan Plateau near Lake Manasarovar. |
| Other Names | Sindhu, Sindh or Mehran |
| Length | 3,180 Kilometres or 1,980 Miles |
| Size of Basin | 11,65,000 Sq. Kilometres or 4,50,000 Sq. Miles. |
| Average Annual Water Flow | 58 cubic miles or 243 cubic kilometres |
| Importance | It serves as the major source of irrigation and food production in Pakistan. Serves as the main source of water resources to Punjab. |
| Reasons For Pollution | Industrial Activities, Industrial waste disposal and Plastic waste. |
About Indus River
Indus River is one of the most important rivers of the Indian Subcontinent. It flows through three different Countries, i.e. India, China and Pakistan. The river Indus originates in the Tibetan Plateau near the lake Manasarovar. After flowing through China and India, it flows through the full length of Pakistan and finally merges with the Arabian sea near Karachi in Sindh.
The level of the river Indus varies throughout the course of its flow. The River Indus has been given different names by the people of Different countries through which it flows. It has names such as Indus, Sindhu, Sindh or Mehran. It is one of the most important rivers of the Indo-Gangetic Plains.
The estimated annual water flow of the river Indus is about 243 cubic kilometres which is twice than that of river Nile and thrice as compared to River Tigris and River Euphrates combined. This makes the river Indus as one of the largest rivers in the world in terms of water flow.
The Indus river serves as a significant source of water supply in Pakistan. It also supports a lot of heavy industries in Pakistan. The Indus acts as an essential source of water supply for Punjab as well.
Indus River History
The river was first described in the Rigveda which was written in 1500 BCE, where it is described by the name of “Sindhu”. The word India comes from Indus as in earlier days India referred to those areas which were located near the east bank of river Indus.
The major Indian Civilizations such as Indus Valley, Harappa and Mahenjodaro were situated on the banks of river Indus which date back to 3,300 BC. Till date around 1,052 settlements have been discovered along river Indus.
The river Indus must have been initiated by the early Tibetan uplift following the collision of India and Asia. The river Indus has remained since the early Eocene Times. The river Indus is still located in its original position and has moved only 100 kilometres east since the early Eocene times.
Indus River Map
The Origin of the river Indus lies in the Tibetan Plateau near the lake of Manasarovar. It arises at the junction of the river Sengge Zangbo and river Gar Tsangpo. The River flows through three countries of the Asian continent which are namely India, China and Pakistan. The overall length of the river is approximately 3,180 kilometres which is nearly 1,980 miles. The total drainage area of the river Indus is around 11,65,000 sq. kilometres.
The river flows from the Tibetan plateau and enters into India through the Ladakh region and flows towards Gilgit-Baltistan. The river Indus then changes its course toward the southern region to enter into Pakistan where it runs along the total length of Pakistan. Finally, it drains into the Arabian Sea near Karachi.
The Northern part of the Indus River and its tributaries lies in the Punjab region of South Asia, while the southern part ends in Sindh in Pakistan. The Indus river feeds the world’s 2nd largest underwater delta which is the Indus Submarine fans. The underwater delta so formed consists of 5 million cubic kilometres of sediment materials eroded by the Indus river in the course of its flow.
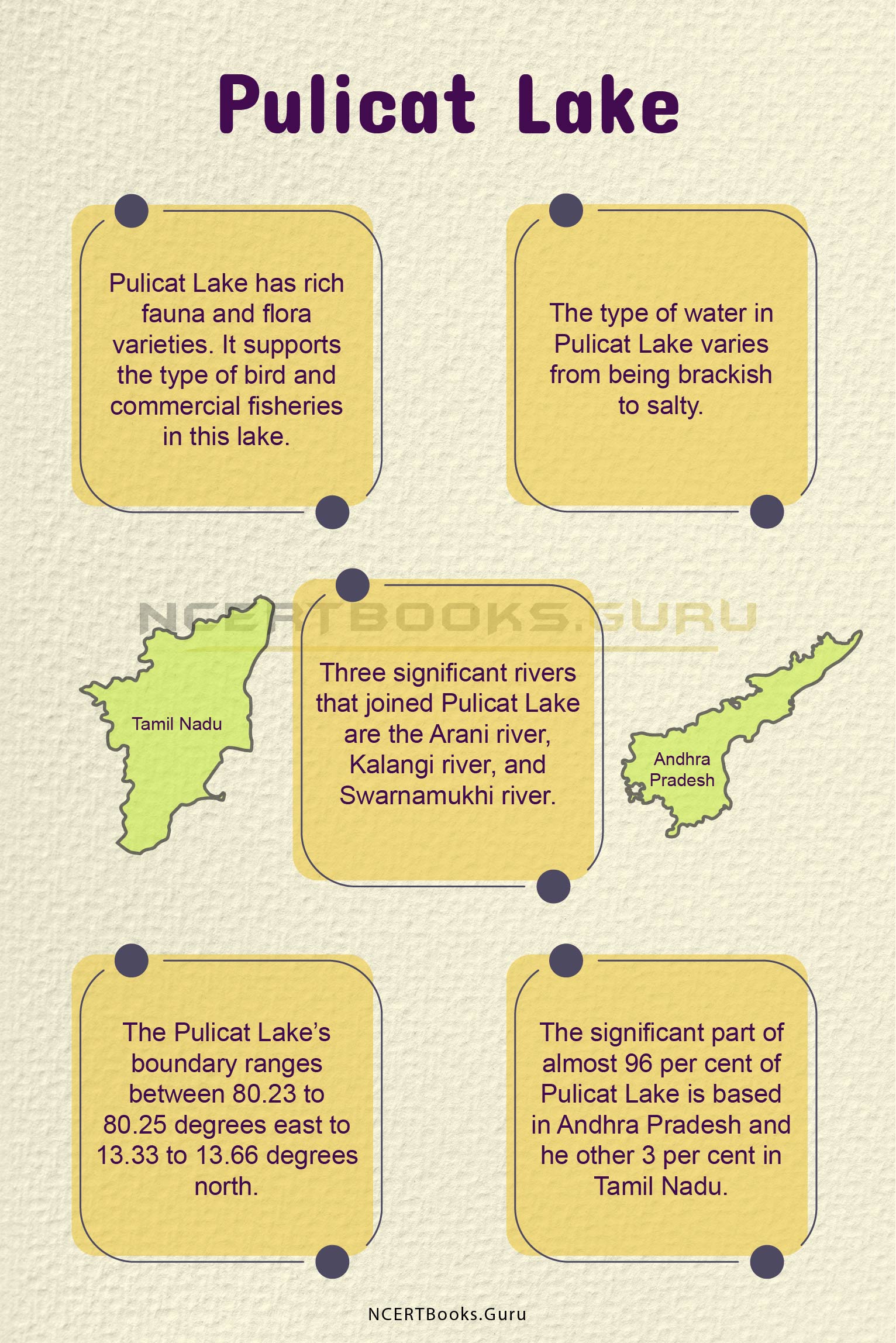
Indus River System
The Indus River is considered as one of the longest rivers of the world in terms of water discharge as it discharges 243 cubic kilometres of water which is twice as compared to the water flow of river Nile. The total length of the Indus river system is around 3180 kilometres. It flows 320 kilometres or 200 miles towards the northwest and enters Ladakh where it joins one of its tributaries, the Zanskar River. Then it continues to flow 240 kilometres before it enters into Pakistan, where it runs along the total length of Pakistan.
The Indus River System has many tributaries that join the river in the course of its flow. The first tributary that joins river Indus is the Zanskar river which is Ladakh. Then the river Indus is joined by the Panjnad river in the left near Punjab which has 5 tributaries of its own, namely, Chenab, Jhelum, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej.
The tributaries that join the river Indus on the right are Shyok, Gilgit, Kabul, Gomal and Kurram. The Indus river system consists of glaciers and snows as it has tributaries that flow through the glaciers of Himalayas, Karakoram ranges and the Hindu Kush mountain ranges.
The width of flow of the river is determined by the seasonal changes, i.e. In winter season the flow of the river diminishes or decreases drastically. While in the rainy season the banks of the river are heavily flooded.
Indus River Pollution
The Indus river serves as the major source of water supply for Pakistan and Punjab. However, with the rapid industrialisation and unmanaged disposal of sewage into the river system has led to the degradation in the quality of water of River Indus. Water pollution in the Indus river is because of many reasons. Out of which the main reason being the dumping of industrial wastes into the river.
The presence of factories near the bank of river Indus as a major cause of pollution of the river. The disposal of industrial wastes in high quantities has led to the death of many aquatic animals in the Indus river, mainly the Indus dolphins.
The other factors that contribute to the pollution in the river Indus are agricultural wastes which include, sodium nitrate, sodium phosphate and other pesticides that increases water pollution. This pollution affects marine animals.
The river is also polluted by unmanaged and untreated wastes that are discharged into it from the cities. The pollution of the Indus has also affected human health in the city of Karachi. Most of the population of Karachi depends on the Indus for drinking water, and boiling the water will not help in reducing chemical wastes. If no proper action is taken to conserve the purity of the river Indus, then it may lead to a drastic downfall in the number of aquatic animals present in the river.
Indus River Importance
River Indus serves as the major source of water for around 180 million people of Pakistan. The river supplies water throughout the year to parts of Punjab and the whole of Pakistan. The agriculture and food production of Pakistan depends mostly on the water supply from river Indus.
The Indus Basin Irrigation System is the most extensive irrigation system ever constructed in the world. This Irrigation system benefits many farmers in Pakistan for agriculture. The Indus River also acts as a medium of transportation for many people.
The Mangla dam built on the river Jhelum and the Tarbela Dam constructed on river Indus acts as a major source of irrigation and flood control. The two dams were built under the Indus Basin Project.
Short Essay on Indus River
India is a land of many rivers, and the Indus river is one of the most important rivers of the Indian Subcontinent. The Indus river originates in the Tibetan Plateau and flows through countries like India, China and Pakistan. The Course of flow of the river ends in the Arabian sea.
The River Indus is considered as the largest river in the world in terms of water flow. The river is approximately 3,180 kilometres in length and has a total drainage area of 11,65,000 km2. The river has different names such as Sindh, Sindhu or Mehran.
The river Indus flows from the Tibetan Plateau and enters India through the Ladakh region. It then enters Pakistan and runs along the full length of Pakistan. The River has many tributaries on both sides. The left tributaries of Indus river are Zanskar river, Panjnad River whose branches are River Jhelum, River Ravi, River Beas, River Sutlej and River Chenab. The right tributaries of river Indus include Shyok, Gilgit, Kabul, Gomal and Kurram rivers.
The Indus River serves as an important source of water supply to Punjab. It is considered as the backbone of water supply for Pakistan. Entire Pakistan depends on the Indus river for irrigation and food production. It also supports many heavy industries in Pakistan.
The River Indus acts as a habitat to a large number of aquatic animals. The Indus river dolphin is the species of dolphin that are found only in the Indus river. The Indus also serves as a home to almost 180 freshwater fish species.
However, the growing industrial activities near the bank of river Indus has highly contributed to its pollution. Unmanaged industrial waste disposal is the main reason for Indus river pollution. The agricultural activities also add to the pollution in river Indus. The pollution has affected the lives of many aquatic animals living in the river. If no action is taken to protect the river water from pollution, it can cause severe damage to all the aquatic animals as well as the humans that consume the water from Indus.

10 Lines on Indus River
- Indus River is one of the most important rivers of the Indo-Gangetic plain in the Indian Subcontinent.
- It is the largest river in the world in terms of water flow. The average annual water flow of River Indus is 243 cubic kilometres.
- The Length of river Indus is approximately 3,180 kilometres.
- The Indus Originates in the Tibetan Plateau and flows through three Asian Countries, that are India, China and Pakistan.
- The Indus Flows through the full length of Pakistan.
- The River Indus has many tributaries on the left as well as on the right side.
- The Indus acts as the main source of water supply for Pakistan.
- The Indus river ends in the Arabian Sea.
- The total drainage area of River Indus is approximately 11,65,000 km2.
- The Indus serves as a home to 180 species of freshwater fish, out of which 22 species of fishes are not found in any other river or sea.
Frequently Asked Questions on Indus River
Question 1.
Where is the Origin of River Indus?
Answer:
The origin of Indus river lies in the Tibetan Plateau near the Mansarovar Lake. It begins at the junction of two rivers, namely, Sengge Zangbo and Gar Tsangpo.
Question 2.
What is the length of River Indus?
Answer:
The Length of river Indus is approximately 3,180 kilometres or 1,980 miles.
Question 3.
What is the importance of Indus river?
Answer:
The Indus river is one of the most important rivers of India as it supplies water to many parts of Punjab and neighbouring states for irrigation and other activities. It also serves as the major source of water supply for Pakistan. The whole of Pakistan depends on the river Indus for irrigation and other agricultural activities.
Question 4.
What are the reasons for pollution of river Indus?
Answer:
The growth of industries in and around the Indus river banks are the major sources of pollution of River Indus. The untreated sewage disposal is also a reason contributing to Indus river pollution.