Kaveri is like a lifeline to two South Indian states- Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, which runs to the Bay of Bengal. It is the basic source of water for utilisation for most purposes, including drinking, electricity, and irrigation. People in South India believe it to be Goddess for the farmers to serve their crops throughout the year. Also, it falls in the category of being holy rivers of India.
Top 10 Largest Rivers in India, you would also find the details about Indian River Systems and major rivers of India.
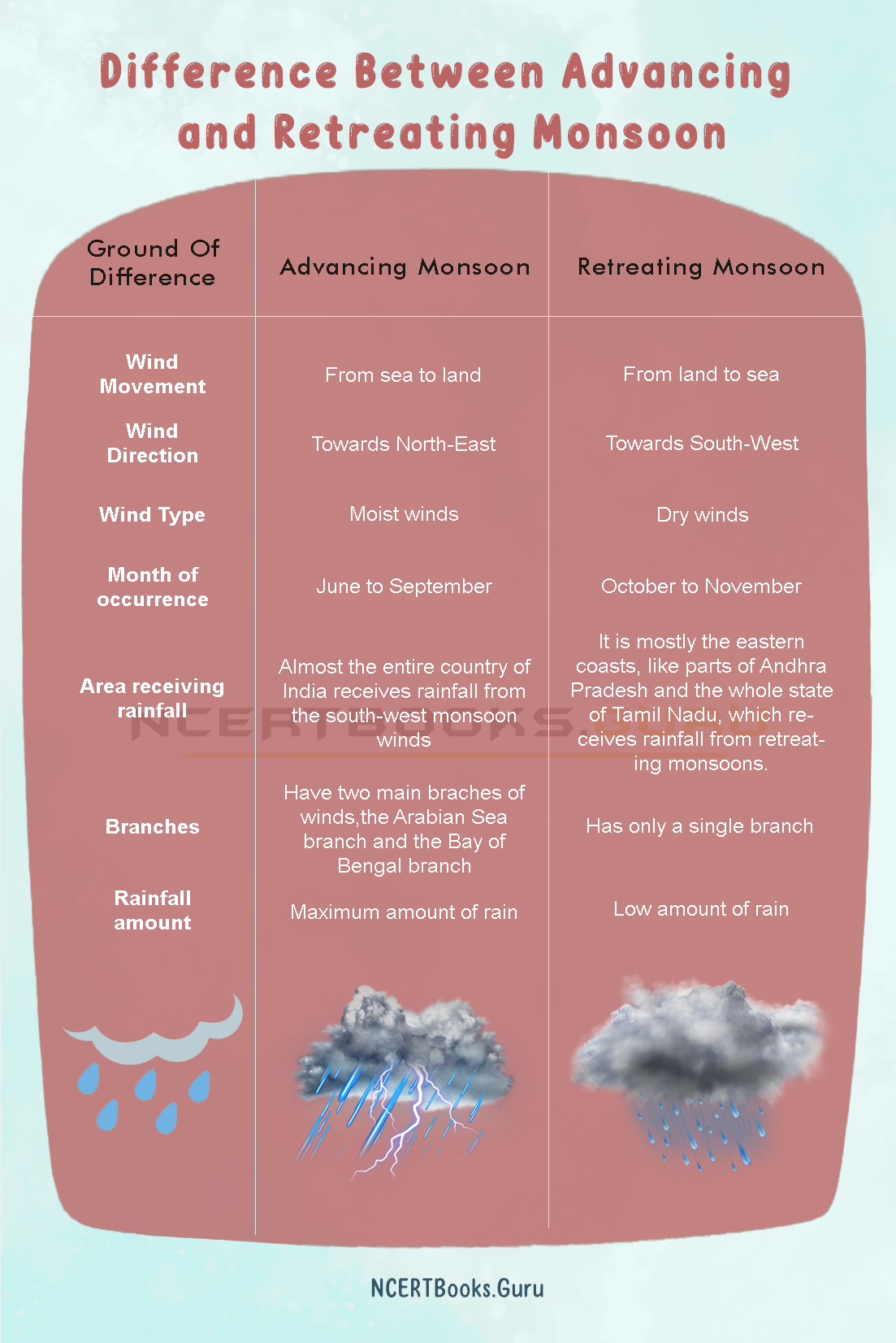
Kaveri River Details
| Name of the River |
Kaveri River |
| Source of Origin |
Talakaveri in Brahmagiri, in Kodagu district, Karnataka |
| Location |
Western Ghats of Karnataka |
| Tributaries |
- Harangi River
- Arkavathi River
- Noyyal River
- Hemavati River
- Kabini River
- Lakshmana Tirtha
- Bhavani River
- Amaravathi River
|
| Length |
800 Kilometer |
| Importance |
Drinking-Water, Domestic Use, Irrigation, Sacred river as Goddess Kaveriamma |
| Pollution |
Domestic water discharge, Nitrates in sediment samples, sewage waste, and agricultural runoff |
About Kaveri River
Kiver Raveri is also famous with the name of River Cauvery, which originates from the Western Ghats in Karnataka in south India. The elevation of the river is 1,341 meters above sea level and flows for 800 kilometres. It flows from Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. People worship it in the name of Goddess Kaveriamma. In South India, it falls as the third largest river after Krishna and Godavari. It has many tributaries flowing along with it.
The direction of the flow of water with Kaveri river is southeast originating from Kodagu district in Karnataka. Also, it flows through the Chamarajanagar district, which gives rise to the island Shivanasamudra. It is the basic source of water for the people residing in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. Also, it is the source of hydroelectricity for them. For centuries, this river serves for irrigating crops. It is like lifeblood to the major cities in the states.
Kaveri River History
Flowing for 800 kilometres before entering the Bay of Bengal, River Kaveri has major historical significance. This river has been a sign of inspiration for major civilizations. The course of River Kaveri is the birthplace for many forms of art, philosophy, and culture. The journey through the Western Ghats from its birth from Talakaveri is believed to high historical and cultural importance. It is an eastern flowing river that forms a delta on the eastern coastline before it falls into the Bay of Bengal.
The history of the Kaveri River is associated with Sivasamudram Waterfalls and Hogennekkal waterfalls. Also, it is famous for The Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary built by its side. The meaning of the river Kaveri is Ponni. Kaveri has major significance for its sacred importance as believed by the people. People of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu associate this river with Goddess Kaveriamma. Thus it has major, major significance in Hinduism.
Kaveri River Map
Kaveri River stretches for 800 kilometres before flowing into the Bay of Bengal. The major part of the river flows through two states of India- Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. It flows for 320 Kilometers in Karnataka and 416 Kilometres in Tamil Nadu. The river flow direction is from North West to South East, built since the 2nd century AD. It is a dense river that forms the delta before joining the Bay of Bengal.
There are several tributaries formed by River Kaveri, which further form small sub-tributaries. Some of the known tributaries formed by river Kaveri in the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are:
- Arakavathy (area covered 4351 sq. km)
- Hemavathy (area covered 5410 sq. km)
- Harangi (area covered 717 sq. km)
- Kabini (area covered 7040 sq. km)
- Shimshal (area covered 8469 sq. km)
- Lakshmana Thirtha
- Suvarnavathy (area covered 1787 sq. km)
Kaveri River System
River Kaveri is the sacred river of South India, which flows over 800 kilometres in the Peninsular region of Western Ghats. It has a great association with Hinduism as Hindus believe it to associate with Goddess Kaveriamma. It falls in the category of holy rivers in India. This river is the basic source of everyday water usage in the two major states of India. Kaveri is an astern flowing river that has a catchment area of around 81,155 square kilometres.
The major part of the river flows from Tamil Nadu, around 420 kilometres, and the rest from Karnataka and Kerala. Over the decades, this river has provided livelihood to many people. The largest temple is built at the place of its origin for Goddess Kaveri.
Kaveri River Pollution
Untreated effluents have been the major cause of polluting river water. Also, Kaveri has become one of the victims of it. This untreated waste becomes the reason for polluting water, which is the major source for domestic use. There have been noticed changes in the Kaveri River due to waste disposal in it over the years.
Not only this, there is one more reason for the cause of water pollution that is depleting forests that resided on the banks of the river. Also, people are disposing of their untreated sewage waste in the river. In the last 20 years, there has been a decline in 28 per cent of forest area on the banks of the river Kaveri. One reason behind such is an urban settlement. It is has deprived of the water quality of the river. The untreated waste from the paper mill of Madhya Pardesh is also one reason for polluting Kaveri water.
Kaveri River Importance
Kaveri River has spiritual and historical importance in India’s history. Karnataka and Tamil Nadu believe it to be a sacred and holy river associated with Goddess Kaveri. Also, a huge temple is built on the river’s birthplace to pay tribute to Goddess Kaveri. Without a doubt, this river has provided livelihood to many people. Also, it has been the basic source of drinking water and for domestic use. This eastern flowing river is the third largest South India river that flows through the Western Ghats from North West to South East.
There are several dams built over Kaveri, and thus it is the basic source of hydroelectricity for the two major states- Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The importance and tales for this river remain unlimited to discuss.
Short Essay on Kaveri River
Kaveri River is the basic source of water for two major states of South India. It provides livelihood to the farmers for irrigation and agriculture. Also, the good number of dams built over the river generates good hydro-power. The river covers three states and a union territory and flows towards the south-east, originating in the Northwest direction.
The origin of the river is at Brahmagiri Hills in Kodagu district of Karnataka. At the origin of the river at Talakaveri, a huge temple is built in association with Goddess Kaveri. Thus for Hindu people, it is a holy and sacred river of South India. Extending to 800 kilometres, this river drains into the Bay of Bengal and forms a delta at its end.
This river forms two islands after it splits in Karnataka- Shivanasamudra, and Srirangapatna. The third island is formed in Tamil Nadu named Srirangam. It is a dense river that spreads over the area of 81,155 sq. km. Major tributaries formed by river Kaveri includes Arakavathy, Hemavathy, Harangi, Kabini, Shimshal, Lakshmana Thirtha, and Suvarnavathy.
The major water source for Banglurur, the IT city, is the Kaveri River, which stores water at Torekandanahalli. The major dams built over the Kaveri River include Upper Anicut in Tamil Nadu, the Krishna Raja Sagar Dam (KRS) built-in Mandya, and three other dams Amaravati Dam, Mettur Dam, and Kalani Dam constructed in Tamil Nadu.

10 Lines On Kaveri River
- Kaveri River is the sacred river of South India that originated from Karnataka and flowed through Tamil Nadu.
- It is the basic water source for irrigation, agriculture, domestic use, and electricity generation in the two states.
- The river extends to 800 kilometres forming a delta before it falls to the Bay of Bengal.
- It is the third-largest South Indian river that gives birth to several tributaries, which further form sub-tributaries.
- Kaveri forms islands of Srirangapatnam and Sivanasamudra in Karnataka.
- It has the greatest importance in Indian history for Hindu people. They associate it with Goddess Kaveri.
- The catchment of the Kaveri River covers the area of 81,155 sq. km.
- The head of the Kaveri river is TalaKaveri, which is the birthplace of the river.
- About 28 percent of forest clearance is observed near the Kaveri River banks for the last 20 years.
- There are many stories associated with Kaveri. However, the tale of Lopamudra is the major one.
FAQs On Kaveri River
Question 1.
From where Kaveri originates?
Answer:
Beginning from Talakaveri, Kodagu district of Karnataka, Kaveri flows through the Western Ghats in the South-East direction. The river flows through the two major South Indian states- Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. Some part of it flows through Kerala and one Union Territory.
Question 2.
What is the historical importance of the Kaveri River?
Answer:
River Kaveri is famous as a holy and sacred river of South India. People, especially in Tamil Nadu, associate it with Goddess Kaveri. Another historical importance of the river is the tale of Lopamudra and Agastya’s Wife.
Question 3.
What is the other name of the Kaveri River?
Answer:
Kaveri has another name as Cauvery. This is an anglicised name of the Kaveri River. This river has been serving people for the past many decades.
Question 4.
What is the name of the Kaveri River in Karnataka?
Answer:
The river is famous with the name of Lopamudra in its origin state. Also, it is famous as Agastya’s Wife. Agastya married Lopamudra for her beauty. He kept Lopamudra hidden in the water pot and hence famous for this historical story.