We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 6 सदाचारः Questions and Answers will cover all exercises given at the end of the chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 6 सदाचारः
अभ्यास के प्ररनौं के उत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
सर्वान् श्लोकान् सस्वरं गायत।
उत्तर
छात्राः श्लोकान् स्वयमेव सस्वरं गायन्तु।
प्रश्न 2.
उपयुक्तकथनानां समक्षम् ‘आम्’ अनुपयुक्तकथनानां समक्षं ‘न’ इति लिखत

उत्तर
![]()

प्रश्न 3.
एकपदेन उत्तरत
(क) कदा शय्यां त्यजेत् ?
उत्तर
प्रातःकाले।
(ख) कानि कृत्वा अध्ययनं कुर्यात् ?
उत्तर
नित्यकर्माणि।
(ग) किं ब्रूयात् ?
उत्तर
सत्यम्।
(घ) केन सह कलहं कृत्वा नरः सुखी न भवेत् ?
उत्तर
मित्रेण।
प्रश्न 4.
रेखाङ्कितपदानि आधृत्य प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत
(क) प्रथमम् ईश्वरं स्मरेत्।
(ख) कलहं कृत्वा नरः दुःखी भवति।
(ग) पितरं कर्मणा सेवेत।
(घ) व्यवहारे मृदुता श्रेयसी।
(ङ) सर्वदा व्यवहारे ऋजुता विधेया।
उत्तर
(प्रश्ननिर्माणम्)
(क) प्रथमं कं स्मरेत् ?
(ख) किं कृत्वा नरः दुःखी भवति ?
(ग) कं कर्मणा सेवेत ?
(घ) व्यवहारे का श्रेयसी ?
(ङ) कदा व्यवहारे ऋजुता विधेया ?
प्रश्न 5.
प्रश्नमध्ये त्रीणि क्रियापदानि सन्ति। तानि प्रयुज्य सार्थक-वाक्यानि रचयत
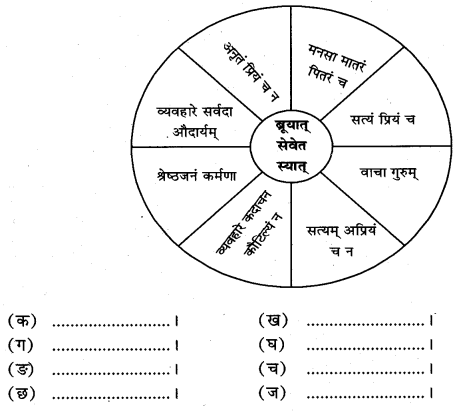
उत्तर
(क) सत्यं प्रियं च ब्रूयात्।
(ख) वाचा गुरुं सेवेत।
(ग) सत्यम् अप्रियं च न ब्रूयात् ।
(घ) व्यवहारे कदाचन कौटिल्यं न स्यात्।
(ङ) श्रेष्ठजनं कर्मणा सेवेत।
(च) व्यवहारे सदा औदार्य स्यात्।
(छ) अनृतं प्रियं च न ब्रूयात्।
(ज) मनसा मातरं पितरं च सेवेत।
प्रश्न 6.
मञ्जूषातः अव्ययपदानि चित्वारिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत
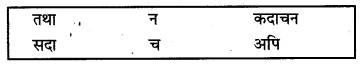
(क) भक्तः …………… ईश्वरं स्मरति।
(ख) असत्यं ………….. वक्तव्यम्।
(ग) प्रियं ……………. सत्यं वदेत्।
(घ) लता मेधा ……………. विद्यालयं गच्छतः।
(ङ) ……………. कुशली भवान् ?
(च) महात्मागाँधी ……………. अहिंसा न अत्यजत्।
उत्तर
(क) भक्तः सदा ईश्वरं स्मरति।
(ख) असत्यं न वक्तव्यम्।
(ग) प्रियं तथा सत्यं वदेत् ।
(घ) लता मेधा च विद्यालयं गच्छतः।
(ङ) अपि कुशली भवान् ?
(च) महात्मागाँधी कदाचन अहिंसा न अत्यजत्।
प्रश्न 7.
चित्रं दृष्ट्वा मञ्जूषातः पदानि च प्रयुज्य वाक्यानि रचयत
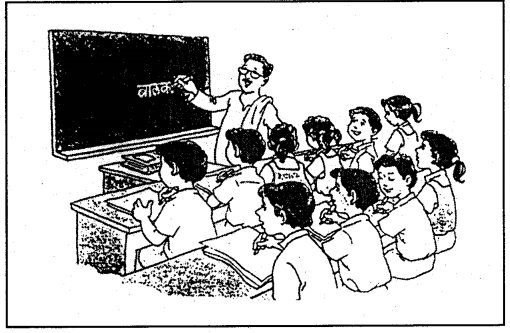

![]()
उत्तर
1. सः शिक्षक: श्यामपट्टे प्रश्नं लिखति।
2. ते छात्राः कक्षायां पुस्तिकायाम् उत्तराणि लिखन्ति।
बहुविकल्पी प्रश्न
(i) कदा शय्यां त्यजेत् ?
(A) प्रातःकाले
(B) सायंकाले
(C) अर्धरात्रौ
(D) मध्याह्ने।
उत्तर
(A) प्रातःकाले
(ii) कानि कृत्वा अध्ययनं कुर्यात् ?
(A) दुष्कर्माणि
(B) नित्यानि
(C) कर्माणि
(D) नित्यकर्माणि।
उत्तर
(D) नित्यकर्माणि।
(iii) किं ब्रूयात् ?
(A) असत्यम्
(B) सत्यम्
(C) कटु
(D) कठोरम्।
उत्तर
(B) सत्यम्
(iv) केनं सह कलहं कृत्वा नरः सुखी न भवेत् ?
(A) कुमित्रेण
(B) मित्रेण
(C) चित्रेण
(D) शत्रुणा।
उत्तर
(B) मित्रेण
(v) प्रथमं कं स्मरेत् ?
(A) धनम्
(B) मित्रम्
(C) अध्यापकम्
(D) ईश्वरम्।
उत्तर
(D) ईश्वरम्।
(vi) किं कृत्वा नरः दुःखी भवति ?
(A) कर्म
(B) कलहम्
(C) परिश्रमम्
(D) अध्ययनम्।
उत्तर
(B) कलहम्
(vii) कं कर्मणा सेवेत ?
(A) पितरम्
(B) पितुः
(C) मातुः
(D) भ्रातरम्।
उत्तर
(A) पितरम्
(viii) व्यवहारे का श्रेयसी ?
(A) कटुता
(B) छलता
(C) मृदुता
(D) बलता।
उत्तर
(C) मृदुता
(ix) कदा व्यवहारे ऋजुता विधेया ?
(A) सर्वदा
(B) प्रातः
(C) सायम्
(D) रात्रौ।
उत्तर
(A) सर्वदा
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 6 सदाचारः Summary Translation in Hindi
1. यस्मिन् देशे य आचार: पारम्पर्यक्रमागतः।
वर्णानां सान्तरालानां स सदाचार उच्यते॥1॥
शब्दार्था:-
आचारः = व्यवहार।
पारम्पर्यक्रमागतः = परम्परा से प्राप्त ।
वर्णानाम् = समस्त वर्गों का।
सान्तरालानाम् = वर्गों के मध्य आए हुए समस्त उपवर्गों का।
सदाचारः (सत् + आचारः) = श्रेष्ठ व्यवहार, सदाचार।
सरलार्थ:-जिस देश में जो व्यवहार परम्परा से आया हुआ होता है उसी व्यवहार को समस्त वर्गों का तथा वर्गों के मध्य आए हुए समस्त उपवर्गों का श्रेष्ठ व्यवहार अर्थात् सदाचार कहा जाता है।
भावार्थः-सदाचार का अर्थ है श्रेष्ठ आचरण। यह आचरण समाज में हमें परम्परा से प्राप्त होता है।
2. प्रातःकाले त्यजेच्छय्यामीश्वरं प्रथमं स्मरेत्।
नित्यकर्माणि कृत्वा च कुर्यादध्ययनं ततः ॥ 2 ॥
शब्दार्थाः- त्यजेत् = छोड़ देना चाहिए।
त्यजेत् + शय्याम् = त्यजेच्छय्याम्।
शय्याम् = बिस्तर को, शय्या को।
प्रथमम् = सबसे पहले।
स्मरेत् = स्मरण करना चाहिए।
नित्यकर्माणि = नित्यकर्मों को, प्रतिदिन किए जाने वाले कर्मों को।
कुर्यात् = करना चाहिए।
अध्ययनम् = पढ़ाई-लिखाई, अध्ययन।
ततः = उसके बाद।
सरलार्थः-प्रात:काल में ही बिस्तर छोड़ देना चाहिए, फिर सबसे पहले ईश्वर का स्मरण करना चाहिए। फिर नित्यकर्मों को करके उसके बाद पढ़ाई-लिखाई करनी चाहिए।
भावार्थ:–प्रात:काल जल्दी उठना चाहिए और फिर सबसे पहले परमात्मा को याद करते हुए उसका धन्यवाद करना चाहिए क्योंकि उसी प्रभु ने हमें यह सुन्दर अनमोल शरीर, सूर्य का प्रकाश, खाने के लिए अन्न, पीने के लिए जल तथा जीवन धारण करने के लिए प्राणवायु प्रदान की है। नित्यकर्म में, दाँत साफ़ करना, स्नान करना आदि आते हैं। इन्हें करने के पश्चात् अपने अध्ययन में जुट जाना चाहिए।
3. सत्यं ब्रूयात् प्रियं ब्रूयात् न ब्रूयात् सत्यमप्रियम्।
प्रियं च नानृतं ब्रूयात् एष धर्मः सनातनः ॥ 3 ॥
शब्दार्था:-
ब्रूयात् = बोलना चाहिए।
प्रियम् = मीठा, प्रिय।
अप्रियम् = दूसरों को अच्छा न लगने वाला।
नानृतम् (न + अनृतम्)। अनृतम् = झूठ।
सनातनः = जो सदा से चला आ रहा हो।
सरलार्थः- सत्य बोलना चाहिए, प्रिय बोलना चाहिए परन्तु अप्रिय सत्य कभी नहीं बोलना चाहिए। दूसरों को प्रिय लगने वाला झूठ भी नहीं बोलना चाहिए। यही सदा से चला आ रहा धर्म है।
भावार्थ:-सत्य बोलना अच्छी बात है परन्तु वह सत्य प्रिय होना चाहिए। जिस सत्य को बोलने से दूसरों के मन में दुःख पैदा हो ऐसा सत्य नहीं बोलना चाहिए। केवल दूसरों को खुश करने के लिए झूठ भी नहीं बोलना चाहिए। सत्य तथा प्रिय बोलना सदाचार का प्रमुख अंग है।
4. सर्वदा व्यवहारे स्यात् औदार्यं सत्यता तथा।
ऋजुता मृदुता चापि कौटिल्यं न कदाचन ॥ 4 ॥
शब्दार्थाः-सर्वदा = सदा, हमेशा।
औदार्यम् = उदारता।
सत्यता = सच्चाई।
ऋजुता = सरलता।
मृदुता = कोमलता।
कौटिल्यम् = कुटिलता, टेढ़ापन।
कदाचन = कभी।
सरलार्थ:-व्यवहार में सदा उदारता, सच्चाई सरलता तथा कोमलता होनी चाहिए। कभी भी व्यवहार में कुटिलता नहीं होनी चाहिए।
भावार्थ:-हमारा व्यवहार सदा ही उदारता, सत्यता से युक्त, सरल तथा कोमल होना चाहिए ऐसे व्यवहार से ही समाज में आदर मिलता है। कभी भी दूसरों के मन को दुखाने वाला या अपने मन में छल-कपट रखकर व्यवहार नहीं करना चाहिए।
5. श्रेष्ठं जनं गुरुं चापि मातरं पितरं तथा
मनसा कर्मणा वाचा सेवेत सततं सदा ॥5॥
शब्दार्था:-
श्रेष्ठं जनम् = अच्छे मनुष्य को, सज्जन को।
मनसा = मन से।
कर्मणा = कर्म से।
वाचा = वाणी से।
सेवेत = सेवा करनी चाहिए।
सततं = निरन्तर, लगातार।
सरलार्थः- सदा ही सज्जन, गुरु, माता तथा पिता की मन, कर्म और वाणी से सेवा करनी चाहिए।
भावार्थ:- सेवा करना सदाचार का महत्त्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है। माता-पिता, गुरुजन तथा सज्जनों की सेवा सच्चे मन से, सच्चे व्यवहार से तथा आदरपूर्ण वचनों से अवश्य करनी चाहिए।
6. मित्रेण कलहं कृत्वा न कदापि सुखी जनः।
इति ज्ञात्वा प्रयासेन तदेव परिवर्जयेत्॥ 6 ॥
शब्दार्था:- मित्रेण = मित्र के साथ।
कलहम् = झगड़ा, कलह।
कृत्वा = करके।
कदापि = कभी।
प्रयासेन = प्रयत्नपूर्वक।
परिवर्जयेत् = छोड़ देना चाहिए।
सरलार्थ:- मनुष्य अपने मित्र के साथ झगड़ा करके कभी भी सुखी नहीं रह सकता। इस बात को जानकर मित्रों के साथ झगड़ने को प्रयत्नपूर्वक छोड़ देना चाहिए।
भावार्थ:- अच्छे लोग सदा प्रेम से रहते हैं कभी आपस में झगड़ते नहीं। मित्र के साथ तो कभी भी झगड़ा नहीं करना चाहिए। क्योंकि मित्र के साथ झगड़ने वाला सदा दुःखी ही रहता है।